Decoding Melanoma: Unveiling a Novel Path to Brain Metastasis
Melanoma brain metastases
Cutaneous melanoma, the deadliest skin cancer, often spreads aggressively, especially to the brain, resulting in rapid progression and limited survival. Molecular understanding of melanoma brain metastases (MBMs) is lacking. Despite similarities in mutational landscapes between MBMs and extracranial tumors, epigenetic drivers remain elusive.
Melanoma exhibits diverse transcriptional states, including de-differentiated, neural crest stem cell-like, melanocytic/differentiated, and transitory states. Targeted therapy alters tumor heterogeneity, leading to more drug-resistant and invasive states. However, the regulation and contributions of these states to tumor progression remain unclear.
HDAC8
HDAC8, a type I histone deacetylase (HDAC), is known for its role in embryonic neural crest cell development and has been implicated in various tumors. The study identifies HDAC8, as a crucial factor driving a stress-induced transcriptional state in melanoma cells, promoting increased metastasis to the brain.
This study demonstrates the crucial role of stress-induced HDAC8 activity in regulating an invasive melanoma cell state that facilitates brain metastasis development. HDAC8 expression rises in melanoma cells under stress conditions, such as UV irradiation, hypoxia, and drug treatment.
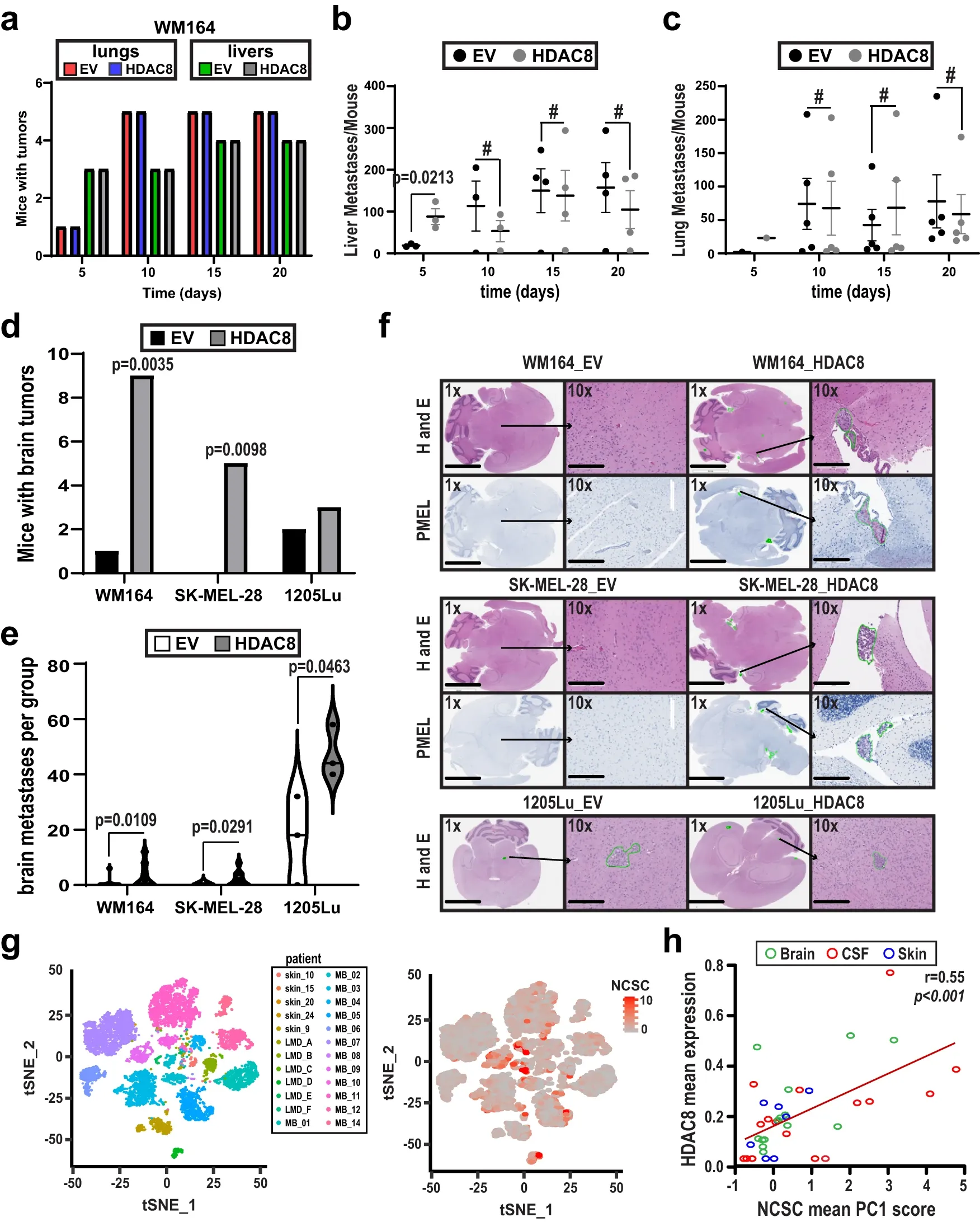
The HDAC8-driven transcriptional state resembles the neural crest stem cell-like state, as confirmed by RNA-seq and ATAC-seq analyses. This state is associated with increased metastatic potential, characterized by an amoeboid phenotype, enhanced invasion, efficient migration through endothelial cell layers and Matrigel, and accelerated seeding to the lungs and brain.
While not replicating the entire brain metastatic cascade, the study models key steps, including cell survival in circulation, infiltration into the brain parenchyma, and macrometastasis establishment. The HDAC8-driven transcriptional state contributes to these processes by increasing cell robustness, invasive capacity, and expression of Serpins, crucial for brain microenvironment adaptation. Additionally, HDAC8 induces a switch to an oxidative phosphorylation metabolic state.
What to expect
Clinical relevance is demonstrated by the association of elevated HDAC8 expression in melanoma samples with decreased overall survival. The study suggests that HDAC8 drives a cell state facilitating increased seeding and initial survival of melanoma cells in the brain through enhanced invasive capacity, improved cell survival, metabolic adaptations, and expression of microenvironmental modulators. The study provides insights into the molecular mechanisms underlying melanoma heterogeneity and highlights HDAC8 as a potential therapeutic target.